As of 2024, nearly two-thirds (65.7%) of U.S. households owned their home, while the remaining portion rented. However, homeownership rates vary significantly across different states and regions, influenced by factors such as affordability, housing availability, and local economic conditions.
Homeownership Rates by State in 2023
A recent analysis by USAFacts, using data from the Census Bureau’s Housing Vacancies and Homeownership portion of the Current Population Survey, highlights the disparity in homeownership rates across states. According to the 2023 data, West Virginia recorded the highest homeownership rate, with 77% of households owning their homes.
One of the primary reasons behind West Virginia’s high ownership rate is the state’s relative affordability.
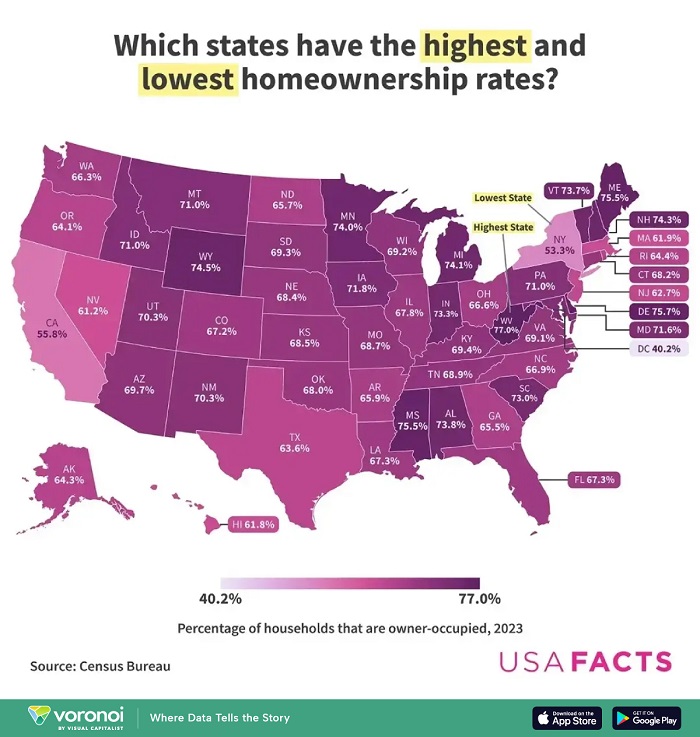 West Virginia consistently ranks among the states with the lowest median home sale prices and has the lowest home price-to-income ratio in the country. Additionally, its largely rural landscape and lower population density contribute to greater housing availability compared to densely populated urban markets.
West Virginia consistently ranks among the states with the lowest median home sale prices and has the lowest home price-to-income ratio in the country. Additionally, its largely rural landscape and lower population density contribute to greater housing availability compared to densely populated urban markets.
States with the Lowest Homeownership Rates
In contrast, states such as Hawaii, California, and New York had some of the lowest homeownership rates in 2023. These states also rank among those with the highest home prices and home price-to-income ratios, making homeownership a more challenging goal for residents.
Urban centers in states like New York and California face high housing demand, a greater proportion of renters due to job concentrations and lifestyle preferences, and stricter zoning regulations that limit housing supply. These factors contribute to lower homeownership rates despite high-income opportunities in these areas.
Key Factors Influencing Homeownership
While affordability remains a critical determinant of homeownership rates, other factors also play a significant role. Housing supply, economic opportunities, and regional job markets all influence whether households can purchase homes. For instance, suburban and rural areas typically have higher homeownership rates than urban centers due to more available land and lower population densities, which lead to lower housing costs.
The data underscores the complexity of the U.S. housing market, where economic conditions, housing policies, and demographic preferences shape homeownership patterns across different regions. Understanding these trends can help policymakers and individuals make informed decisions about housing investments and urban planning.
Source: www.visualcapitalist.com





































