Most countries have, for many decades, kept a record of their own critical minerals list.
For example, the U.S., drew up a list of “war minerals” during World War I, containing important minerals which could not be found and produced in abundance domestically. They included: tin, nickel, platinum, nitrates and potash.
Since then, as the economy has grown and innovated, critical mineral lists have expanded considerably. The Energy Act of 2020 defines a critical mineral as:
“A non-fuel mineral or mineral material essential to the economic or national security of the U.S., whose supply chains are vulnerable to disruption.” — ENERGY ACT, 2020.
Currently there are 50 entries on this list and the U.S. Geological Survey (USGS) estimates that China is the leading producer for 30 of them. From USGS data, we visualize China’s share of U.S. imports for 10 critical minerals.
The U.S. is 100% import-reliant for its supply of yttrium, with China responsible for 94% of U.S. imports of the metal from 2018 to 2021.
A soft silvery metal, yttrium is used as an additive for alloys, making microwave filters for radars, and as a catalyst in ethylene polymerization—a key process in making certain kinds of plastic.
China is a major supplier of the following listed critical minerals to the U.S.
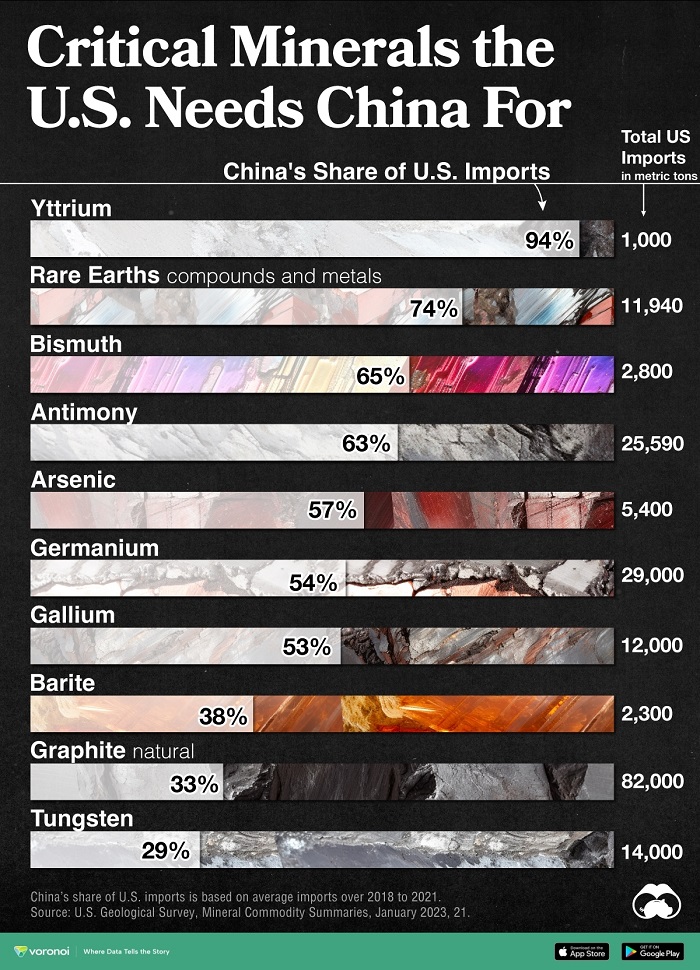
Meanwhile, the U.S. also imports nearly three-quarters of its rare earth compounds and metals demand from China. Rare earth elements—so called since they are not found in easily-mined, concentrated clusters—are a collection of 15 elements on the periodic table, known as the lanthanide series.
Source: www.visualcapitalist.com




































